I don't think that I did so well on the Gas Laws quiz. I know that for the test, I'll need to study the different laws closer, and notice the differences between them. I missed a day, and totally had no clue what STP was, which seems pretty important now.
STP
EFellows28 My Chemistry
Tuesday, May 10, 2016
Air Bag Lab
We had to construct an air bag... one that would save our passenger's life but also not hurt the passenger from being too full of air.
Here's what we decided to do...
http://chemistry.about.com/od/chemicalreactions/f/What-Is-The-Equation-For-The-Reaction-Between-Baking-Soda-And-Vinegar.htm
Here's what we decided to do...
- Find maximum volume of the bag
- Fill bag with water
- pour H2O into a graduated cylinder--- Volume H2O=Volume CO2
- Calculate to determine amount of NaHCO3 needed
- Volume from step 1, convert to L
- Looking for NaHCO3... n=PV/RT
- solve for moles of CO2
- use stoich to find grams of NaHCO3
- Baking soda=vinegar 1:1 molar ratio
- Use D of vinegar to find volume of vinegar
- x.20 because vinegar is only 5% acetic acid
- Multiply measurements by .65 to not completely fill up the bag (or explode it)
http://chemistry.about.com/od/chemicalreactions/f/What-Is-The-Equation-For-The-Reaction-Between-Baking-Soda-And-Vinegar.htm
PVNRT
PV=nRT
R=universal gas constant .0821 L atm/ mol K
EX. Calculate the pressure in atm exerted by 1.82 mol of Sulfur Hexaflourine gas in a steel vessel with a volume of 5.43 L at 69.5 degrees C (+273.15)
PV=nRT
P= nRT/V
(1.82 x .0821 x 342.65)/ 5.43
=9.43 atm
http://www.phscale.net/idealgaslaw.htm
http://www.westfield.ma.edu/cmasi/gen_chem1/Gases/ideal%20gas%20law/pvnrt.htm
R=universal gas constant .0821 L atm/ mol K
PV=nRT
P= nRT/V
(1.82 x .0821 x 342.65)/ 5.43
=9.43 atm
http://www.phscale.net/idealgaslaw.htm
http://www.westfield.ma.edu/cmasi/gen_chem1/Gases/ideal%20gas%20law/pvnrt.htm
Measuring Pressure
Common units of pressure:
688mmHg x (1atm/760mmHg) = .905 atm
http://www.sengpielaudio.com/ConvPress.htm
- Pascal Pa
- Avg Air pressure at sea level 101,325
- Kilopascal kPa
- Avg Air pressure at sea level 101.325
- Atmosphere atm
- 1 exactly
- Millimeters of Mercury mmHg
- 760 exactly
- Inches of Mercury inHg
- 29.92
- Torr torr
- 760 exactly
- Pounds per square inch psi
- 14.7
688mmHg x (1atm/760mmHg) = .905 atm
http://www.sengpielaudio.com/ConvPress.htm
Boyle's Law
TELLS THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN PRESSURE AND VOLUME IN AN INVERSE RELATIONSHIP
P1V1=P2V2
Ideal gas at low pressure holds strictly to this relationship
http://www.wisegeek.org/what-is-boyles-law.htm
https://www.boundless.com/chemistry/textbooks/boundless-chemistry-textbook/gases-5/gas-laws-51/boyle-s-law-volume-and-pressure-254-8360/
P1V1=P2V2
Ideal gas at low pressure holds strictly to this relationship
http://www.wisegeek.org/what-is-boyles-law.htm
https://www.boundless.com/chemistry/textbooks/boundless-chemistry-textbook/gases-5/gas-laws-51/boyle-s-law-volume-and-pressure-254-8360/
Calculating Heat...
Q=MCΔT
Q= Heat in Joules
M= Mass in grams
C= Specific Heat
ΔT= Change in Temperature
EXAMPLE:
Calculate the amount of energy in joules required to heat 454 grams of water from 5.4 degrees C to 98.6 degrees C. Calculate the amount of energy in calories, too.
Q=?
M=454 g
Tinitial=5.4 degrees C
Tfinal=98.6 degrees C
c= 4.184 J/gdegC
Q=454x4.184x(98.6-5.4)
Q=1.77x10^5 Joules or 177 KJ
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4RkDJDDnIss
http://www.wikihow.com/Calculate-Specific-Heat
http://chemistry.about.com/od/workedchemistryproblems/a/Specific-Heat-Example-Problem.htm
Q= Heat in Joules
M= Mass in grams
C= Specific Heat
ΔT= Change in Temperature
EXAMPLE:
Calculate the amount of energy in joules required to heat 454 grams of water from 5.4 degrees C to 98.6 degrees C. Calculate the amount of energy in calories, too.
Q=?
M=454 g
Tinitial=5.4 degrees C
Tfinal=98.6 degrees C
c= 4.184 J/gdegC
Q=454x4.184x(98.6-5.4)
Q=1.77x10^5 Joules or 177 KJ
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4RkDJDDnIss
http://www.wikihow.com/Calculate-Specific-Heat
http://chemistry.about.com/od/workedchemistryproblems/a/Specific-Heat-Example-Problem.htm
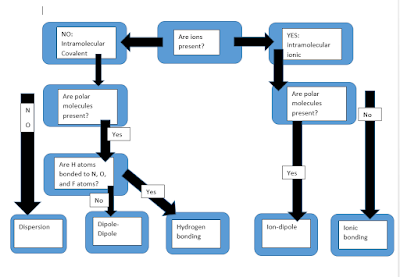
Intra/Inter Molecular Forces
I made this diagram to help with intramolecular and intermolecular forces... hope it's helpful...
http://chemed.chem.purdue.edu/genchem/topicreview/bp/intermol/intermol.html
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)

.jpg)